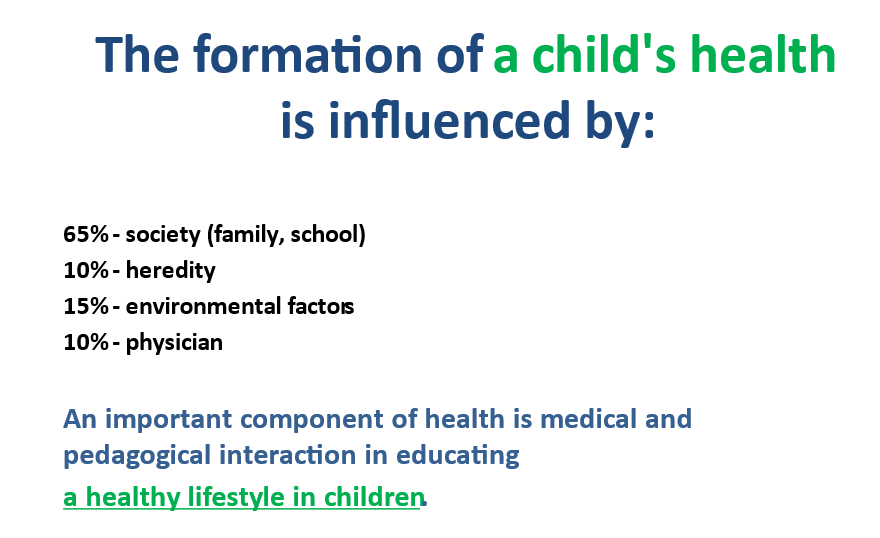
What are the factors of child health?
The Periods of a Childhood
As a legal terminology, “childhood” continues from birth until age 18. But a baby’s life starts from the moment of fertilization. We have to know three different periods of life which are found in the medical literature. They all play a key role in the formation of a child’s health.
- Prenatal (Intrauterine period): 270 days from the moment of fertilization to the birth of a child. In other words, can be called – a pregnancy;
- Intranatal period: from 2 – 4 hours up to 18-20 hours, from the time of appearance of the uterus contractions until the ligation of the umbilical cord;
- Postnatal (Extrauterine period): in pediatrics – from birth to 18 years
As a pediatrician, I have dealt just with the last one – the postnatal period. Let`s proceed to the topic of extrauterine life when the baby is born.
1.1 Classification of childhood periods

Try to remember these “Ages and Stages” as they are important for the formation of a child’s health:
1 – Neonatal period: in medical contexts, newborn or neonate (from Latin, neonatus) refers to an infant in the first 28 days after birth:
- early neonatal period – the first 7 days after birth,
- late neonatal period – from 8 until 28 days of life;
2 – Infancy – the term infant is typically applied to young children between the ages of 1 month and 12 months;
3 – Toddlers (young children) – a toddler is a child between the ages of 1 year and 3 years. The toddler years are a time of great cognitive, emotional and social development. The word is derived from “to toddle”, which means to walk unsteadily, like a child of this age;
4 – Preschool children: children from 3 years until 5 years;
5 – Young school-age children: 6-10-year-old children;
6 – Older school-age children: 11-18-year-old children.
Why are these “Ages and Stages” so important for us? Every period of a child`s life is characterized by their peculiarities of growth and development, which you can read below. That is why, if you do not have time to read all materials, you should concentrate just on the age at which you are interested. And then step by step together and consecutively with growing your baby, you will learn more and more from this website. All methods and tactics of care and feeding your baby, which is presented in other articles, are based on the peculiarities of ages.
1.2. Peculiarities of Child’s Ages & Formation of a child’s health
The first 28 days after a child’s birth (neonatal period) are very crucial because newborns are particularly vulnerable and require very thorough care during this time. This’s a process when the baby adapts to the conditions of extrauterine existence, hence the basic functions of the body are in a state of unstable equilibrium. This is due to the immaturity of the central and peripheral nervous system; braking processes predominate over excitation processes (the newborn usually sleeps 20 – 22 hours a day).
Incomplete development of the organism may lead to the following states: physiologic jaundice, physiological drop in body weight, physiological mastitis, urate infarction, and others. Given these facts, a newborn requires very careful care, compliance with the required sanitary conditions for their life, and compulsory breastfeeding.
The first 3 years of a child’s life are characterized by rapid growth and development.
In the first year of life, infants experience a fast pace of physical development – a child’s body mass doubles in the first 4-5 months and triples in 12 months, and they grow up by 23-25 cm for the first year. They also experience a fast pace of neuropsychological development: development of all the sensory activities; formation of positive emotions and motor activity; speech development; development of mental functions: attention, memory, and thinking. Waking length increases from 30 – 40 minutes in one month to 2.5 – 3 hours by the end of the year.
They have relative weakness in some functional organs and systems against the background of intense growth and development that can lead to an increased multiplicity of acute diseases to deviations in health (exudative diathesis, rickets, anemia, various disorders of nutrition, etc.). Low resistance to the variety of acute diseases owing to weakening of the original passive immunity produced from the mother, and still the absence of acquired immunity. This information is very important for understanding: why we should avoid visiting public places and traveling with our small babies. It is not forbidden, but if you want to take a risk, you can travel with your child at this age.
The second year of life is the beginning of the formation of complex brain functions, and the rapid development of speech.
The higher nervous activity is improved (by the beginning of the second year, the child can stay awake for 5 hours), and the sensory perception (ability to differentiate various forms, sizes, colors, etc.) is improved.
Physical activity continues to improve as well: by the age of two the child is well walking, and movements occupy a large place in his life.
Children are easily excitable and find it difficult to adapt to changes in living conditions. Their nervous system is in the stage of becoming and developing, which is why they are very vulnerable to changes in environmental conditions.
Resistance of the child’s organism to various pathogenic influences remains sharply lowered. Therefore at this age, children in comparison with children in the first year of life are more susceptible to acute infectious diseases.
The recommended daily schedule for this age group: Up to 1,5 years, children sleep during the day 2 times: the first sleep 2,5-2,0 hours, the second 2,0-1,5 hours. Night sleep 10-11 hours. The waking period lasts 3,5 – 4,0 hours.
After 1,5 years, children sleep in the daytime 1 time 3,0-3,5 hours. Night sleep 10-11 hours. The waking period gradually increases from 5,0 hours to 6,0 hours by the end of the 2nd year.
By the 2nd year, a child must already eat, dress and undress independently.
In the third year of life, the child slows down the intensity of physical development, which is typical for the first two years of life.
Increases the efficiency of the nervous system (the duration of wakefulness increases to 6 – 6,5 hours).
There is a further development of speech, sensory, and tentative-cognitive activity, and the movements are being perfected. Vocabulary is rapidly increasing. Speech at this age becomes the main means of communication with adults and with each other.
The body’s resistance to the external environment’s harmful effects gradually increases as well as the physical endurance of children as a result of the further formation of immunity.
The recommended daily schedule for this age group: from the age of three, daytime sleep is usually 1 time, with an average duration of 2,0-2,5 hours.
The waking period gradually increases from 5 hours to 6,5 hours by the end of the 3rd year. Active wakefulness is 6,0-6,5 hours.
Night sleep 10-11 hours.
The number of feedings – 4 times a day.
For mandatory lessons (drawing, modeling, designing, music, physical education) the maximum duration of the lesson is 25-30 minutes. Why these lessons are obligatory? Firstly, these exercises are important for the development of the muscles of the hands, which will prepare your child for writing skills. Secondly, it is important for the development of the concentration of attention, and memory. Furthermore, it is also important to remember not to overdo it, classes should not be long, and your kid is not ready for them yet. Here the principle is important: regularly and gradually, gradually step by step increase the duration of the load.
Why is it important? – I will tell in the following chapters of my book: the features of the child’s physical and neuropsychological development. Knowing all these features, it will be very easy for you to look after, educate and communicate with your favorite child.
It is very important to start at this age the formation of self-service skills, helping adults with household chores, for example, when laying a table, preparing for classes on caring for plants, and pets, working in the garden, some sports activities, and so on.
I will tell you a secret: Swimming increases children’s mental abilities. According to the results obtained by American and Australian scientists, early training in swimming not only strengthens the health and immunity of the baby but also stimulates the development of his motor skills, as well as mathematical abilities. Researchers of the Griffith Institute have studied children from different countries (Australia, USA, and New Zealand) for three years. They conducted observations related to the development of children. For more than 7,000 children under the age of five participated in the swimming training program.
It has been established that children who have been taught swimming from an early age overtake the majority of their peers in intellectual development; the level of their mental abilities exceeds the average. Children who can swim are much better than their peers, and master such skills as drawing different forms, cutting applications from paper, painting pictures, and demonstrating the development of visual-motor skills. Better than their “land” peers, children solved mathematical and grammatical problems. Their speech was also more developed. Sexual differences were not found. Swimming exercises equally stimulate the mental abilities, of both girls and boys.
Improving these abilities will help children be more successful in school, better adapt to society, and be more self-confident. Researchers compared other indicators, for example, the socioeconomic status of parents. As shown by comparative studies, swimming lessons – have more impact on the level of intellectual development than the financial situation of the family.
Conclusions
The rapid pace of development of all organs and systems and the incompleteness of immunity contribute to the fact that young children become sick due to even insignificant violations in nutrition and hygienic care and at contact with any infectious agent.
At the same time, each acute infectious disease transferred can lead to the development of chronic diseases and entail a backlog in the child’s physical or neuropsychological development that may negatively affect the formation of a child’s health.
The contribution of the adult in ensuring the normal development of young children is huge and significant. Health and harmonious development of the child is provided only if the tasks of physical, mental, moral, and aesthetic education are performed.
If you liked this article about the formation of a child’s health, please leave your comment below!






Pingback: (2022) How Do Physical Exercises Affect Learning? Connective Tissue And Hippocampus Secrets | Childhealthcreation.com | How To Grow A Healthy Child?
Pingback: (2023) How Does Insufficient Water Intake Affect The Child´s Health And Adequate Brain Function? | Childhealthcreation.com | How To Grow A Healthy Child?